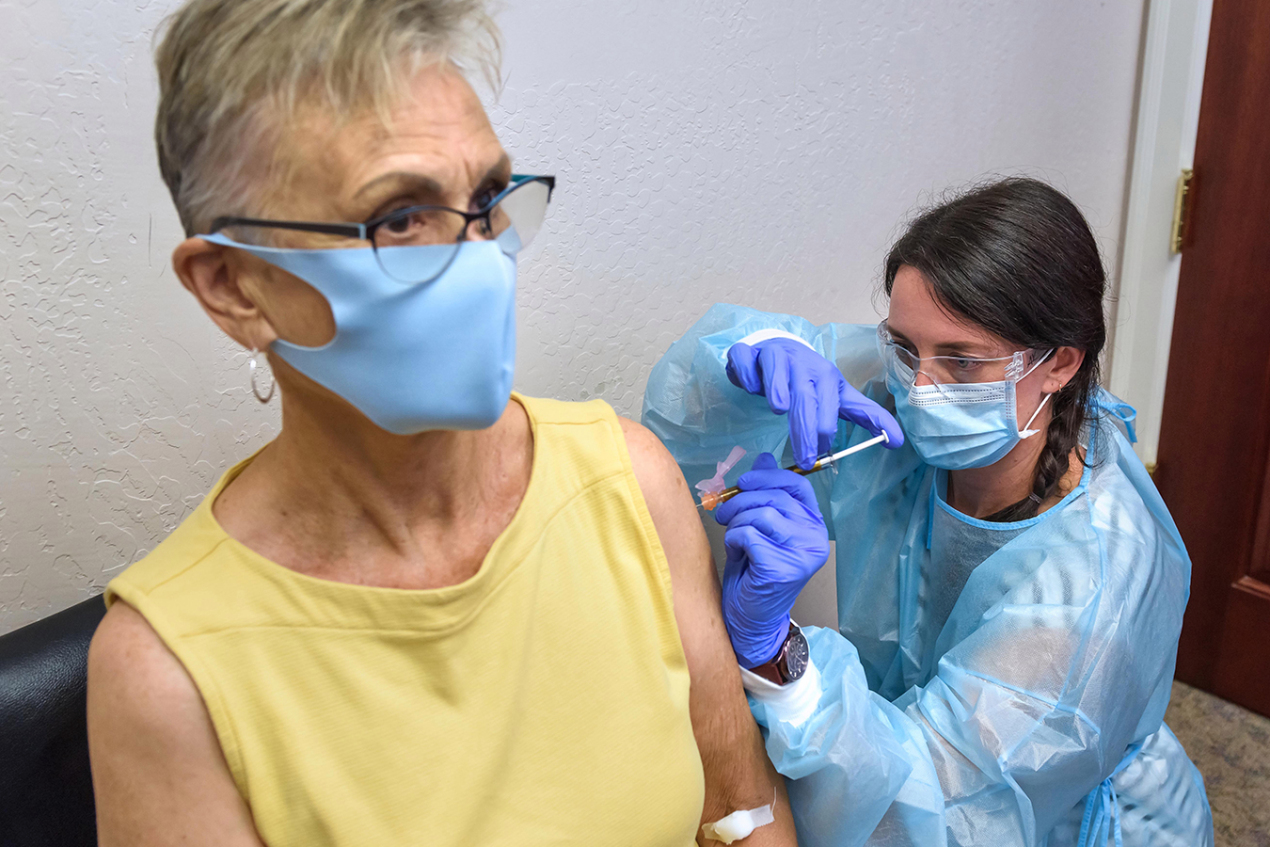
Since July, the institute has been one of the staging grounds for a quest to find a vaccine for the novel coronavirus, which causes a disease that has killed more than 700 people in Oregon, more than 230,000 in the US, and 1.2 million worldwide. And inside, Gregg Lucksinger, the interim medical director of the institute, taps a business card against an oval wooden table in a brightly lit corner room. He leans back in an office chair and reminisces about the lessons learned in Liberia, where he worked in an Ebola treatment unit in 2015. He hopes those lessons will aide him and his colleagues now.
“In [Liberia], the epidemic overwhelmed health systems…. It was really fascinating to see that,” he says. “And that’s what we’re struggling with in the United States to prevent from happening. We’ve been really on the edge in a few places.”
Lucksinger’s work in clinical research began in Austin, Texas, during the HIV epidemic of the 1980s. He went on to help develop vaccines and/or therapeutics for HIV, hepatitis C, and Ebola.
Now, another complicated and highly contagious virus threatens humanity. Lucksinger and the institute in Oregon are working on two Phase 3 COVID-19 vaccine trials. The first, produced by biotech startup Moderna (which has been proven to reduce the risk of COVID-19 infection by 94.5 percent), has wrapped up its enrollment period and moved to data collection, a process by which research coordinators follow up with volunteers to see if they’ve developed symptoms of or contract the coronavirus as they go about their daily lives. This stage could take a year or two. The second trial is for a vaccine produced by Novavax. Under the White House’s Operation Warp Speed (OWS), a $10 billion initiative, COVID-19 vaccine and therapeutic trials have been accelerated, compressing what typically takes years into months. By running various processes in parallel and increasing the number of volunteers from a couple hundred to at least 30,000 for each trial, OWS hopes to have a vaccine by early 2021.